Let's Understand
- Vraj Shah

- Feb 11, 2022
- 6 min read
Operating Syste

In simple layman language, an Operating System(short form:-OS) is a software that makes the computer hardware to work. Computer hardware just provides raw computer power, the OS is responsible for making the computer power useful for users.
In technical terms :- An operating system is a program that controls the execution of application programs and acts as an interface between the user of a computer and the computer hardware.
Alternate Simple Understanding:- Operating system is the one program running at all times on the computer (usually called the kernel), with all else being application programs.
SUMMARY: -OS is the master program which controls major functionalities of a Computer.

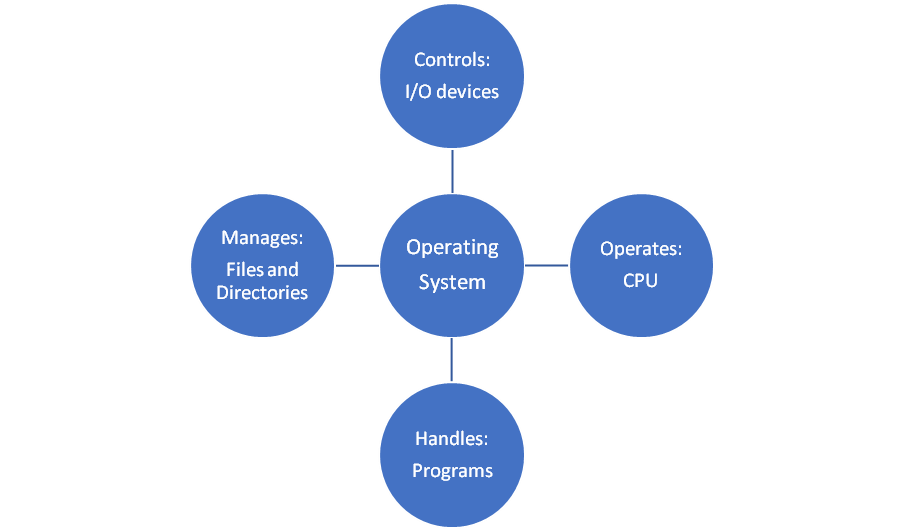
Features of OS
Resource Management: When parallel accessing happens in the OS means when multiple users are accessing the system the OS works as Resource Manager, its responsibility is to provide hardware to the user. It decreases the load in the system.
Process Management: Manages various processes running in a computer system. A process is basically a program, ran by a user while using a computer. For eg. Microsoft Word is word processor program which is managed by the OS to run smoothly.
Storage Management: It manages the memory resources of the computer. The memory resources are:-
Primary Memory (RAM)(Random access memory)
Secondary Memory(eg. CD, Hard Disk,etc.)
All the programs are loaded in the main memory before execution. OS manages how much memory to be allotted to each program in the main memory.
Security/Privacy Management: Privacy is also provided by the Operating system by means of passwords so that unauthorized applications can’t access programs or data. For example, Windows uses Kerberos authentication to prevent unauthorized access to data.
Device management: It also manages the peripheral devices like mouse, printer, etc. It interacts with these devices using Device Drivers.It’s primary task is to manage I/O operations from the user end.
Visual summary of features of OS:
Every Computer Device needs an OS for its functioning. Examples of some OS :- MS, Dos, Windows XP, Widows Vista, Unix, Linux, etc.
Functions of O.S. at micro - Level
Process Management: Process management involves the execution of various tasks such as creation of processes, scheduling processes, management of deadlocks and termination of processes. When a process runs in a computer system, a number of resources such as memory and CPU of the computer system are utilised. It is the responsibility of an operating system to manage the running processes by performing tasks such as resource allocation and process scheduling. The operating system also has to synchronise the different processes effectively in order to ensure consistency or shared data.
Generally. only a single process is allowed to access the CPU for its execution at a particular instant of time. When one process is being processed by the CPU, the other processes have to wait until the execution of that particular process is complete. After the CPU completes the execution of a process, the resources being utilised by that process are made free and the execution of the next process is initiated. All the processes that are waiting to be executed are said to be in a queue. In some cases, a computer system supports parallel processing allowing a number of processes to be executed simultaneously.
A process consists of a set of instructions to be executed called process code. A process is also associated with some data that is to be processed. The resources that a process requires for its execution are called process components. There is also a state associated with a process at a particular instant of time called process state.
Similar to these concepts are a number of concepts associated with process management of an OS. Some are listed below:-
Process state
Process control block(PCB)
Process Synchronization
Process Synchronization
Deadlock
Memory Management:Memory Management function of an OS helps in allocating the main memory space to the processes and their data at the time of their execution. Along with the allocation of memory space, memory management, also perform the following activities;
Upgrading the performance of the computer system.
Enabling the execution of multiple processes at the same time.
Sharing the same memory space among different processes
Memory Management is one of the most important functions of OS because it directly Affects the execution time of a process. The execution time of the process depends on the availability of data in the main memory. Therefore, an OS must perform the memory management in such a manner, that the essential data is always present in the main memory. An effective memory management system ensures accuracy, availability and consistency of the data imported from the secondary memory to the main memory.
An effective Memory Management system must ensure the following:
Correct relocation of data: The data should be relocated to and from the main memory in such a manner that the currently running processes are not affected. For eg. If two processes are sharing a piece of data, then memory management system must relocate this data only after ensuring that the two processes are no longer referencing the data.
Protection of data from illegal change: The data present in the main memory should be protected against unauthorised access or modifications. The memory management system should ensure that a process is able to access only that data for which it has the requisite access and it should be prohibited from accessing data of other processes.
Provision to share information: An ideal memory management system must facilitate sharing of data among multiple processes
Utilization of small free spaces: A Memory Management system should be able to apply appropriate defragmentation techniques in order utilize small chunks of scattered vacant spaces in the main memory.
File Management:File management is defined as the process of manipulating files in a computer system. A file is a collection of specific information stored in the memory of the computer system. File management includes the process of creating, modifying and deleting the files. The following are some of the tasks performed by the file management function of operating system:
It helps in creating new files and placing them at a specific location.
It helps in easily and quickly locating the files in the computer system.
It makes the process of sharing the files among different users easy.
It helps store the files in separate folders known as directories that ensure better organisation of data.
It helps modify the content as well as the name of the file as per the user's requiement.
The below shows the general hierarchy of file storage in an operating system

Device Management:Device management is another important function of the operating system. Device management is responsible for managing all the hardware devices of the computer system. It may include the management of the storages devices as well as the management of all the input/output devices of the computer system. It is the responsibility of the operating system to keep a track of the status of all the devices in the computer system. The status of any computer device, internal or external, may be either free or busy. If a device requested by a process is free at a specific instant of time, the operating system allocates it to the process. An operating system manages the devices in a computer system with the help of device controllers and device drivers.

Security Management: The security management function of an operating system helps in implementing mechanisms that secure and protect the computer sysrtem internally as well as externally. Thereofore, an operating system is responsible for securing the system at two different levels, which are internal security and external security.
Internal security refers to the protection of activities of one process from the activities of another process. The term internal security may also be regarded as system protective. The internal security of the computer system also ensures the reliability of the computer system. There may be a number of processes running in the computer system concurrently. It is the responsibility of the operating system to make sure the only one process at a time his access to a particular resource of the computer system. Most of the operating systems use the concept of least privilege to implement internal security.

External security refers to the implementation of mechanisms for securing the data and programs stored in the computer system as well as the various resources of the computer system against unauthorised access. External security may also be regarded as system security. External security in particularly required when a computer system is either on a network or connected to the Internet. It is easier for the operating system to implement the security mechanisms for accidental security breaches. Most of the external security mechanisms implemented by the sperating system are only to prevent the computer system against accidental misuse.. The various external test, accidental or intentional, to the computer system may include reading, writing or deletion of computer data by an unauthorised user and accessing of computer resources on devices by an unauthorised user. It is not possible to prevent the computer system from external threats only at the operating system level. Apart from the operating system, the three other major levels at which external security should be implemented are physical, human and network. The most common external security mechanism emplayed by most operating systems is a software firewall. The software firewall is software included in the operating system that is specially designed to prevent the computer system against unauthorised users or programs from gaining access to the data and programs stored in the computer system.
Let me conclude by clarifying one myth:
O.S cannot make hardware faster. However it can make h/w appear faster
Can't wait to see you all next time around!



Comments